What is the main cause of Congestive heart failure?
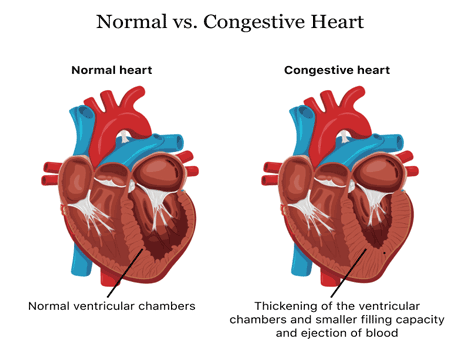
Cardiologists use the term congestive
heart failure (CHF) to describe a patient whose heart does not pump enough blood to the rest of
the body to meet the body's energy demand.
Coronary artery disease is the most common cause of congestive heart failure. High levels of
cholesterol and/or triglycerides in the blood are risk factors for coronary artery disease. Blood
pressure is high.
It's generally better to repair the Valve if it’s in healthy condition and done by Balloon
Valvuloplasty. If the condition of the valve is not such that it can be repaired or the patient's
condition is not that it can go for By-Pass surgery then the Best option is Valve Replacement.
Causes of Congestive Heart Failure
Congestive heart failure can be caused by
one of two factors.
The heart muscle pumps well in this situation, but the blood route is inefficient. It happens when too
much blood flows to the lungs, causing the lungs and, eventually, the heart to struggle. This occurs
with certain types of holes or connections that some babies are born with. With these connections (also
known as shunts), blood that has already returned from the lungs to the heart filled with oxygen ends up
back in the lungs and then back in the heart. These are some examples of these types of lesions:
- A patent ductusarteriosus is a blood vessel that connects the aorta to the main pulmonary artery in foetal life but usually closes within the first few days of life. If it is too large and does not close, the baby will have an abnormally high amount of blood flow to the lungs. This is a common issue in premature infants.
- A large ventricular septal defect (VSD), or a hole between the two lower pumping chambers of the heart, is another issue that causes excessive blood flow to the lungs.
Symptoms of Congestive Heart Failure
Signs of heart failure can appear in anyone at any age, even in young children that may be born with heart defects. However, it usually affects older people who have weakened hearts due to other diseases.
Among the symptoms are:
- Rapid breathing and bluish skin
- Asthmatic-like breathing spasms and wheezing
- Older people experience more disorientation, brain fog, and confusion.
- Fainting, dizziness, weakness or fatigue
- Being easily tired
- Anxiety, suffocation, and restlessness are common symptoms.
- Hacking, dry cough that worsens when lying down
- Urinating more frequently during the night
- Hacking, dry cough that worsens when lying down
- Suffering from nausea, abdominal swelling, tenderness, or pain (may result from the buildup of fluid in the body and the backup of blood in the liver)
- Swelling (Edema) caused by fluid buildup, particularly in the feet, ankles, and legs
- Weight gain due to fluid retention or weight loss due to poor nutrient absorption and decreased appetite
How to Prevent Congestive Heart Failure -
The best way to avoid congestive heart failure is to avoid the conditions that contribute to it, or to
manage these conditions carefully if they develop.
Better yet, don't start smoking. It plays a significant role in the arterial damage that can lead to
heart failure. Avoid secondhand smoke as well.
Eat heart-healthy foods. Foods that are beneficial to you contain little saturated fat, Trans fat,
sugar, or sodium. Consider fruits and vegetables, low-fat dairy, lean protein like skinless chicken, and
"good" fats like olive oil, fish, and avocadoes. Eat Smart provides practical ideas for eating for heart
health.
If you are overweight, you should lose weight. Along with diet, physical activity aids in achieving this
goal and is also beneficial to your heart.
Diagnosis
There is no single test that can be used to diagnose heart failure. Your medical history, family history, a physical exam, and the results of various tests will all be considered by your doctor. The answer is yes.
- Electrocardiogram (EKG): A non-invasive test that provides information about the electrical activity of your heart, such as how fast it beats and whether you've had previous heart attacks.
- Chest X-ray: A picture of the heart, lungs, and other chest structures that shows if the heart is enlarged or if there is lung damage.
- BNP blood test: BNP (B-type natriuretic peptide) is a hormone that is used to determine the severity and prognosis of heart failure.
- An echocardiogram is a heart ultrasound image. It differs from another test called a Doppler ultrasound, which depicts blood flow to the heart and lungs.
Treatment of congestive heart failure
There is no treatment for heart failure. The goal of treatment is to alleviate symptoms and prevent further damage. The specific treatment plan is determined by the stage and type of heart failure, underlying conditions, and the individual patient. The following elements may be included in a treatment plan:
Lifestyle changes. These are the same changes that are used to prevent heart failure. In addition, you may be advised to avoid salt (because of fluid retention) and caffeine (because of heartbeat irregularities). Your doctor will advise you on how much fluid to drink and what types to drink, as fluid intake should be limited at times.
Medications
There are numerous medications available to treat the symptoms of congestive heart failure. They are as follows:
ACE inhibitors: These reduce the workload on the heart by relaxing the arteries and lowering blood pressure. MRAs are drugs that block hormones produced by the adrenal glands that can harm the heart.
Diuretics: These medications help relieve ankle swelling, fluid retention, and shortness of breath caused by heart failure. Diuretics aid in the removal of water and salt from the body. Loop and thiazide diuretics are the two main types.

